极智AI | 多模态大模型中的动态高分辨率
动态分辨率技术允许模型根据输入图像的复杂度和处理需求,实时调整其处理的分辨率。在处理简单或者信息量较少的图像时,模型可能会采用较低的分辨率以减少计算量;在处理复杂或者细节丰富的图像时,模型则会采用更高的分辨率以捕获更多细节。
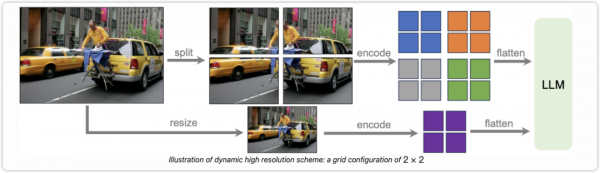
下面是 LLava-Next 中动态高分辨率的实现示意图,其实就是两个分支,一个是 split 切图,一个是 resize 直接对大图进行缩放,这是为了保留全局的语义信息。对于视觉编码模型的输入来说,动态高分辨率的切图比如切 4 张图,完了还要再加上 resize 的那张图,这样其实是 5 张图的输入。
从代码实现来说,下面的动态高分辨率的代码实现来自 InternVL2 的图片预处理,主要就是对动态高分辨率的处理,
# 忽略导入IMAGENET_MEAN = (0.485, 0.456, 0.406)IMAGENET_STD = (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)def build_transform(input_size):MEAN, STD = IMAGENET_MEAN, IMAGENET_STDtransform = T.Compose([T.Lambda(lambda img: img.convert('RGB') if img.mode != 'RGB' else img),T.Resize((input_size, input_size), interpolation=InterpolationMode.BICUBIC),T.ToTensor(),T.Normalize(mean=MEAN, std=STD)])return transformdef find_closest_aspect_ratio(aspect_ratio, target_ratios, width, height, image_size):best_ratio_diff = float('inf')best_ratio = (1, 1)area = width * heightfor ratio in target_ratios:target_aspect_ratio = ratio[0] / ratio[1]ratio_diff = abs(aspect_ratio - target_aspect_ratio)if ratio_diff < best_ratio_diff:best_ratio_diff = ratio_diffbest_ratio = ratioelif ratio_diff == best_ratio_diff:if area > 0.5 * image_size * image_size * ratio[0] * ratio[1]:best_ratio = ratioreturn best_ratiodef dynamic_preprocess(image, min_num=1, max_num=12, image_size=448, use_thumbnail=False):orig_width, orig_height = image.sizeaspect_ratio = orig_width / orig_height# calculate the existing image aspect ratiotarget_ratios = set((i, j) for n in range(min_num, max_num + 1) for i in range(1, n + 1) for j in range(1, n + 1) ifi * j <= max_num and i * j >= min_num)target_ratios = sorted(target_ratios, key=lambda x: x[0] * x[1])# find the closest aspect ratio to the targettarget_aspect_ratio = find_closest_aspect_ratio(aspect_ratio, target_ratios, orig_width, orig_height, image_size)# calculate the target width and heighttarget_width = image_size * target_aspect_ratio[0]target_height = image_size * target_aspect_ratio[1]blocks = target_aspect_ratio[0] * target_aspect_ratio[1]# resize the imageresized_img = image.resize((target_width, target_height))processed_images = []for i in range(blocks):box = ((i % (target_width // image_size)) * image_size,(i // (target_width // image_size)) * image_size,((i % (target_width // image_size)) + 1) * image_size,((i // (target_width // image_size)) + 1) * image_size)# split the imagesplit_img = resized_img.crop(box)processed_images.append(split_img)assert len(processed_images) == blocksif use_thumbnail and len(processed_images) != 1:thumbnail_img = image.resize((image_size, image_size))processed_images.append(thumbnail_img)return processed_imagesdef load_image(image_file, input_size=448, max_num=12):image = Image.open(image_file).convert('RGB')transform = build_transform(input_size=input_size)images = dynamic_preprocess(image, image_size=input_size, use_thumbnail=True, max_num=max_num)pixel_values = [transform(image) for image in images]pixel_values = torch.stack(pixel_values)return pixel_values
这段代码其实就是主要就是两个过程,首先是寻找最接近的宽高比,也就是 find_closest_aspect_ratio 函数在做的事情,然后就是动态预处理,包括了切割和缩放,最后进行拼接,结束,等待送入视觉编码模型。
好了,以上分享了 多模态大模型中的动态高分辨率,希望我的分享能对你的学习有一点帮助。
好文章,需要你的鼓励
CES上杨元庆首谈AGI,碾压人类的叙事不会让AI更聪明
很多人担心被AI取代,陷入无意义感。按照杨元庆的思路,其实无论是模型的打造者,还是模型的使用者,都不该把AI放在人的对立面。
清华大学字节跳动首创视频换脸新纪元:让照片主角完美融入任何视频场景
这项由清华大学和字节跳动联合开展的研究首次实现了高保真视频换脸技术的重大突破。DreamID-V框架通过创新的身份锚定视频合成器和多模态条件注入机制,成功解决了传统视频换脸技术中身份相似度低、时间不连贯等核心问题,在保持原视频动作表情的同时实现完美的身份替换,为影视制作、创意设计等领域带来革命性变化。
Gmail新增Gemini驱动AI功能,智能优先级和摘要来袭
谷歌宣布对Gmail进行重大升级,全面集成Gemini AI功能,将其转变为"个人主动式收件箱助手"。新功能包括AI收件箱视图,可按优先级自动分组邮件;"帮我快速了解"功能提供邮件活动摘要;扩展"帮我写邮件"工具至所有用户;支持复杂问题查询如"我的航班何时降落"。部分功能免费提供,高级功能需付费订阅。谷歌强调用户数据安全,邮件内容不会用于训练公共AI模型。
阿尔伯塔大学新突破:让AI学会自我检查错误,准确率远超人工审核
阿尔伯塔大学研究团队开发出名为Gnosis的AI自我检查系统,能让人工智能实时监测自己的内部"思维状态",判断答案可靠性。该系统通过分析AI的隐藏状态和注意力模式,在数学推理任务中达到95%准确率,超越传统方法和大型审核模型,且仅需500万参数。更重要的是,它能在AI回答40%时就预测最终答案质量,支持早期错误检测,为构建更诚实可靠的AI系统开辟了新路径。







